With the rise of electric vehicles, it might seem that noise pollution from automobiles is on the decline. However, 80% of car noise comes from the contact between tires and the road, with poor road conditions significantly amplifying this noise. To tackle this issue, Thomas Antoine, Expert Leader in Noise & Vibration Technology at Renault Group, developed the Apache program. This initiative maps road conditions to identify areas where repairs could significantly reduce noise pollution, benefiting the environment, economy, and public health. Antoine, along with Fadila Hrird, a master’s student in geomatics at CY Cergy Paris Université, elaborates on the technology and its benefits.
Thomas Antoine, who has been with Renault Group since 2018, highlights the pressing issue of noise pollution. The World Health Organization reports that 20 million Europeans suffer from noise-related issues, with 8 million experiencing sleep disturbances. Ademe, the French Agency for Ecological Transition, estimates the social cost of road noise in France at 80 billion euros annually.
READ MORE: Porsche Unveils High-Performance Panamera Turbo S E-Hybrid and Panamera GTS
To combat noise pollution inside vehicles, car manufacturers are increasingly using active sound control technology, commonly found in audio headphones. This technology uses sensors around the vehicle to detect road noise and emit sound waves that cancel out these noises, enhancing the in-car experience. Renault Group, driven by a culture of innovation, extends this technology further with the Apache program.
The Apache program, or Auscultation du Profil Acoustique des Chaussées et de leur Efficacité énergétique, uses a sensor that analyzes road conditions much like a vinyl needle. It creates detailed maps of the acoustic state of road networks, highlighting areas in need of repair. “This technology not only improves the acoustics inside our vehicles but also aids communities in making precise decisions regarding road repair budgets,” explains Antoine.
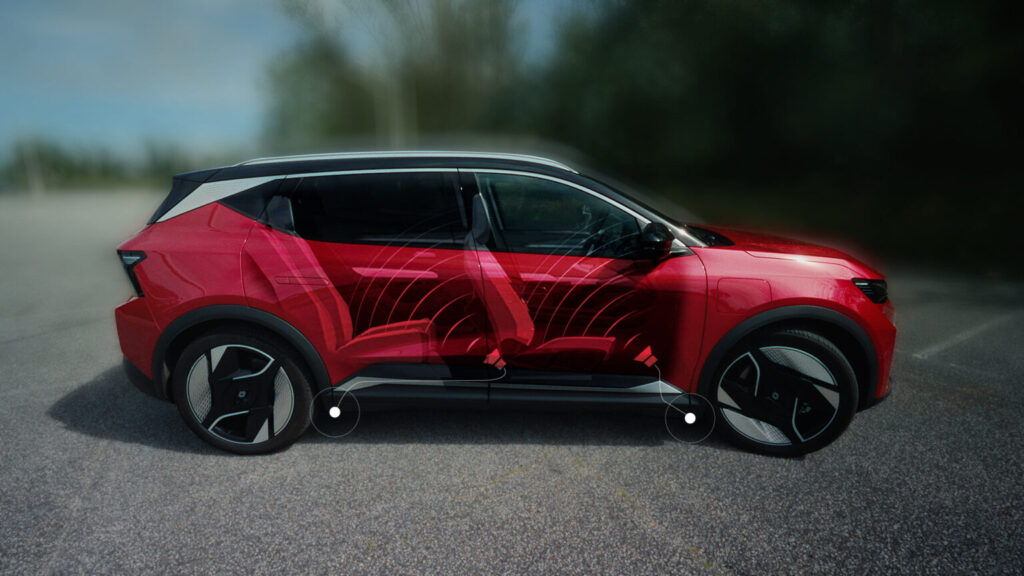

To enhance these maps, Antoine collaborated with Fadila Hrird, a geomatics engineer. Hrird integrates various data layers, including proximity to sensitive locations like schools and hospitals, to assess the impact of road conditions on residents. The collaboration with Bruitparif, the Noise Observatory for Île de France, adds traffic data, essential for understanding road deterioration rates and noise pollution levels. This partnership enabled successful testing in Saint-Quentin-en-Yvelines, leading to the program’s expansion across Île de France with around thirty vehicles equipped with Apache sensors.
The Apache program, patented by Renault Group and awarded a Golden Decibel by the National Noise Council, has attracted interest from cities in France and abroad. It demonstrates a clear link between noise pollution and CO2 emissions, quantifying environmental savings from road resurfacing. For instance, resurfacing the Paris ring road could reduce noise levels significantly and become a “white” carbon operation within 3.5 years, thanks to annual CO2 savings of 16,000 tons.
Antoine sees this project as a pivotal shift for Renault Group, creating new value chains by focusing on non-traditional areas. Hrird, representing a new generation of engineers, anticipates future applications of AI to process increasing data volumes, enhancing the relevance and impact of projects like Apache.
READ MORE: Lexus LBX Named Best Compact Hybrid SUV in EcoCar Electrified Top 50
Subscribe today for the freshest car news delivered to your inbox




